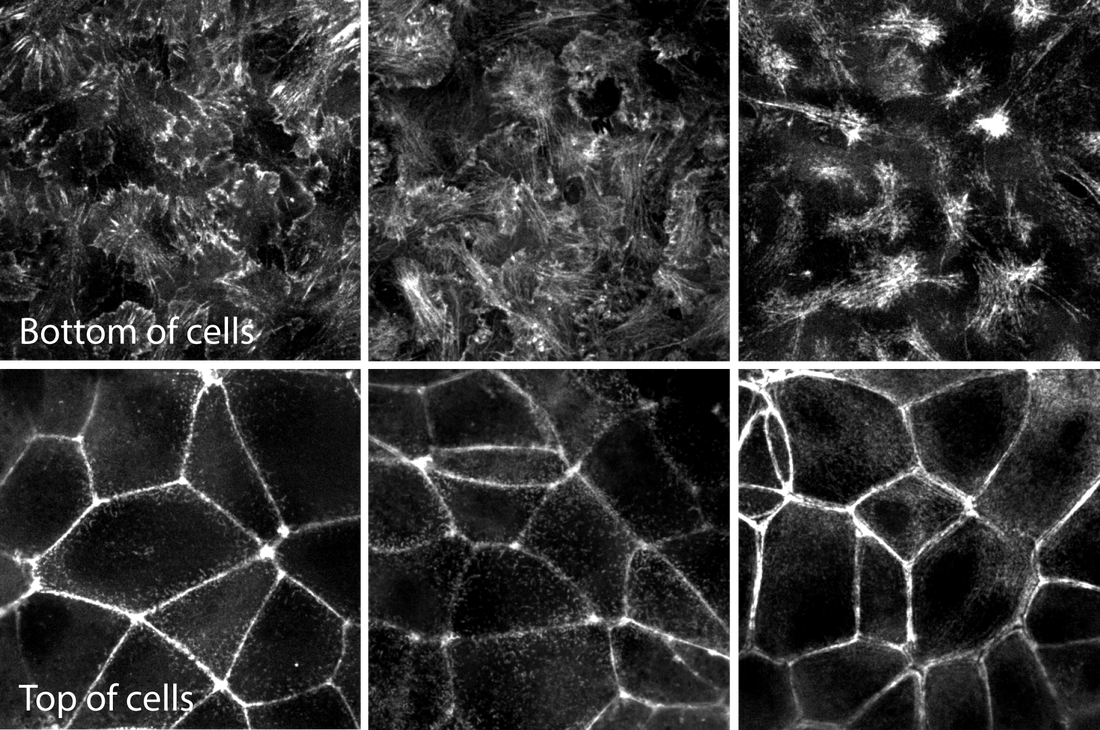
Figure. Movies of ß-actin, α-actinin & actinomyosin in various actin structures. Top row movies: Z-stacks of live hiPS cells expressing mEGFP-tagged ß-actin (left), α-actinin (center) and non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIB (right) imaged on a spinning-disk confocal microscope. Images start from the bottom of the cells and end at the top. Figure 2. Images of the bottom and top of each structure for easier comparison. Representative images of mEGFP tagged ß-actin (left), α-actinin (center) and non-muscle myosin heavy chain IIB (right) from the bottom (top row) and tops (bottom row) of cells. These images are single slices taken from the z-stacks above. Observations
Actin - ß-actin
Actin bundles - α-actinin
Actomyosin bundles - Myosin IIB
In summary, α-actinin localizes to a subset of actin (e.g. the actin bundles) and myosin IIB to a yet smaller subset (actomyosin bundles) as expected. The general localization pattern of actin containing structures is consistent with an apical-basal epithelial polarity in these cells. |
AboutObservations and descriptions from the microscope Archives
February 2019
Categories
All
|
The Institute |
Legal |
Help & contact |
Follow Us
|
Copyright © 2024 Allen Institute. All Rights Reserved.
|
|
See more on alleninstitute.org
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed