Movie. Z-stack of live hiPS cell colony expressing mEGFP-tagged Histone H2B type 1-J protein. Cell Mask Deep Red Plasma Membrane dye was applied to mark cell boundaries (magenta). NucBlue Live Ready Probe Reagent was used to compare mEGFP-tagged H2B localization (left panel) to a NucBlue Live (Hoechst) DNA stain (left panel). Cells were imaged in 3D on a spinning-disk confocal microscope. Movie starts at the bottom of the cells and ends at the top. Scale bar, 5µm. Observations
Observations
Movie. Z-stack and timelapse movie of nucleoli. The left panel shows a Z-stack of a live hiPS cell colony expressing mEGFP-tagged nucleophosmin. Cells were imaged in 3D on a spinning-disk confocal microscope. Right panel is the same image as the left but with contrast enhanced to visualize dimmer localization in mitotic cells. Movie starts at the bottom of the cells and ends at the top. Scale bar = 5µm. Movie. Z-stack and timelapse movie of nucleoli. Timelapse movie of a live hiPS cell colony expressing mEGFP-tagged nucleophosmin. Cells were imaged on a spinning-disk confocal microscope every 3 min. Image is a maximum intensity projection through the volume of the cells. Frames were histogram matched to adjust for photobleaching. Movie plays at 900x real time. Scale bar = 5 µm.
Observations
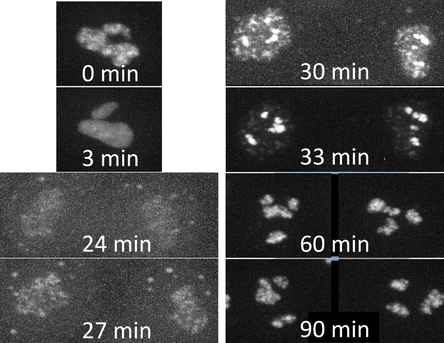
Figure 1. Movies of fibrillarin in Nucleoli. Left: Z-stack of live hiPS cells expressing mEGFP tagged fibrillarin imaged on a spinning-disk confocal microscope. Images start from the bottom of the cells and end at the top. Right: Timelapse movie of live hiPS cells expressing mEGFP tagged fibrillarin. Images were collected in 3D every 3 minutes for 1.5 hours on a spinning-disk confocal microscope. Image is a maximum intensity projection. Playback speed is 900x real time. Figure 2. Time series of cell division. A single cell going through cell division taken from the movie on the right. Observations
Figure. Timelapse movies of hiPSC cells expressing mEGFP tagged Lamin B1. Images were collected in 3D every 3 minutes for 12 hours (left) or every 35 seconds for 23 minutes (right) on a spinning-disk confocal microscope. Images are maximum intensity projection (left) or single slices from the middle of the z-stack (right). Playback speed is 1800x (left) and 350x (right) real time.
Observations
|
AboutObservations and descriptions from the microscope Archives
February 2019
Categories
All
|
The Institute |
Legal |
Help & contact |
Follow Us
|
Copyright © 2024 Allen Institute. All Rights Reserved.
|
|
See more on alleninstitute.org
|

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed